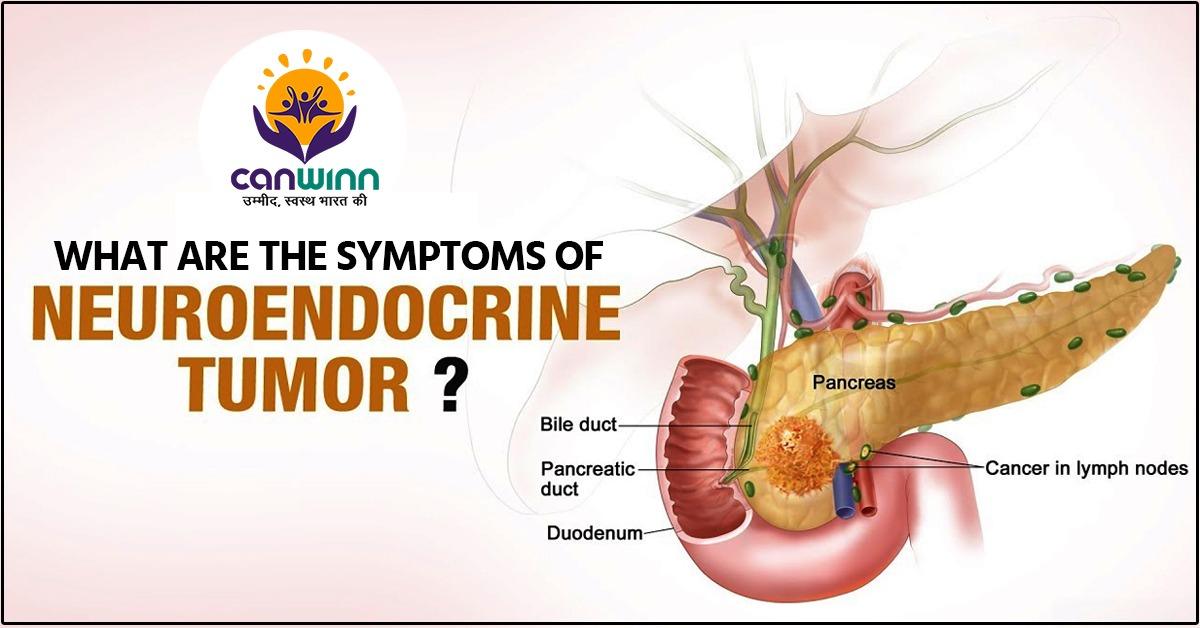
What Is a Neuroendocrine Tumor?
Human bodies carry specialized cells called neuroendocrine cells that function same as the nerve cells and hormone-producing cells. Thus, neuroendocrine tumors are the cancers that arise in these cells. They are the rarest kind of tumors that mostly occurs in the appendix, lungs, pancreas, small intestine, and rectum.
Neuroendocrine tumors are of various types in which some develop gradually while some grow very hastily. Moreover, some types of these tumors produce excess hormones and some don’t even release hormones. Therefore, these nonfunctional neuroendocrine tumors do not cause any symptoms.
Symptoms of Neuroendocrine Tumors
Neuroendocrine tumor symptoms depend upon its type, therefore, below are the tumor-related symptoms that a patient might experience:
General cancer symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained weight loss
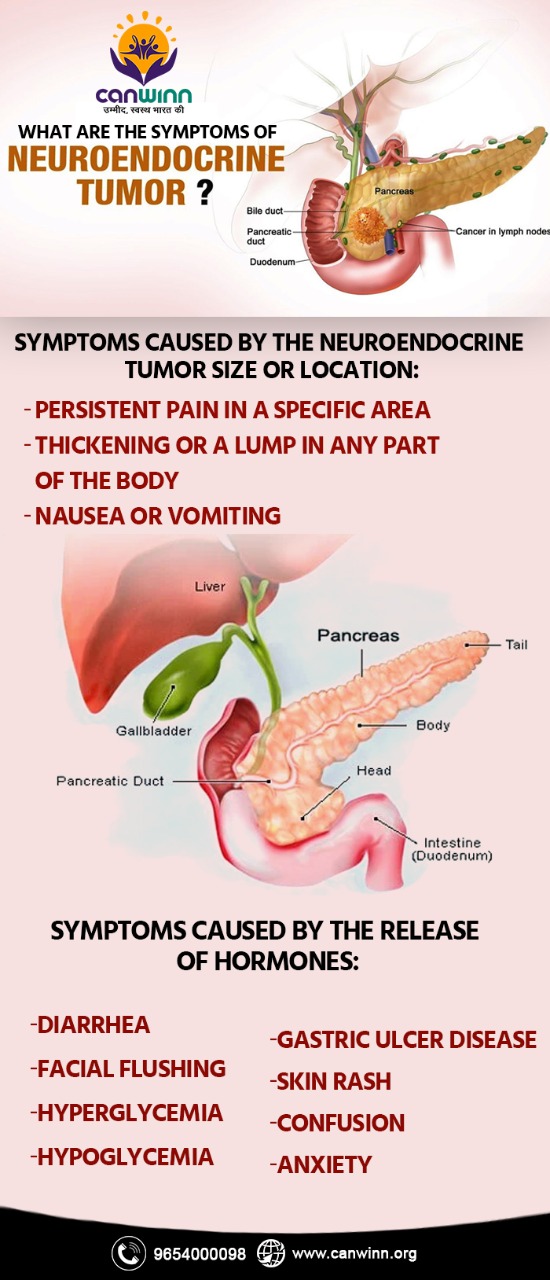
Symptoms caused by the tumor size or location:
- Persistent pain in a specific area
- Thickening or a lump in any part of the body
- Nausea or vomiting
- A cough or hoarseness that does not go away
- Changes in bowel or bladder habits
- Jaundice, which is the yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes
- Unusual bleeding or discharge
Symptoms Caused by the Release of Hormones:
- Diarrhea
- Facial flushing (without sweating)
- Hyperglycemia
- Hypoglycemia
- Gastric ulcer disease
- Skin rash
- Confusion
- Anxiety
Carcinoid syndrome
When the neuroendocrine tumors release hormones, they are known as functional tumors. Most commonly, when the neuroendocrine tumors in small intestine and lungs spread to another part of the body, Carcinoid syndrome occurs. Carcinoid syndrome produces serotonin that can breed one or more than one symptom or sign.
Serotonin transforms into 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) which can be easily measured in the urine. However, carcinoid syndrome cannot surely be diagnosed alone with these symptoms.
Some of the possible symptoms of Carcinoid syndrome are:
- Facial flushing
- Diarrhea
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing or asthma-like symptoms
- Unexplained weight gain
- Weakness
- Fast heartbeat
- Heart murmur
- High blood pressure
- Carcinoid heart disease
In addition, alcohol or stress could make the symptoms of this syndrome worse. The foods also trigger the syndrome. These foods contain lots of Amines, such as yeast extracts, aged cheeses, tofu, and smoked fish and meats.
OR
Serotonin, like walnuts, plantains, pecans, bananas, and tomatoes.
Carcinoid crisis
Carcinoid crisis is the life-threatening form of Carcinoid syndrome. It occurs patients undergo rigorous and immediate symptoms of carcinoid syndrome. The symptoms of Carcinoid crisis involves dangerous fluctuations in blood pressure and heart rate.
Is Neuroendocrine Cancer Aggressive?
As we have mentioned earlier, some of the neuroendocrine tumors grow very slowly but some kinds of neuroendocrine tumors are the aggressive cancers that result in attacking and destroying normal body tissue. In addition, they can spread to other parts of the body that is called metastasizing.
Neuroendocrine tumor diagnosis
Generally, the neuroendocrine tumor diagnosis will include:
- Physical exam
- Tests to look for excess hormones
- Imaging tests
- Biopsy (Procedures to remove a sample of cells for testing)
Treatment
The treatment for neuroendocrine tumors completely depends on the location, kind, and hormones-related signs of the disease.
Following are the general options for the treatment of neuroendocrine tumor:
Surgery: This treatment includes removing the tumor as much as possible.
Chemotherapy: It includes strong drugs that are intended to kill tumor cells. The process to give the drugs will be either through a vein in the arm or as a pill. Doctors also recommend Chemotherapy after the surgery to eliminate the risk of reoccurrence of a tumor.
Targeted drug therapy: When doctors directly focus on specific abnormalities present within tumor cells, they use targeted drug therapy. This treatment kills tumor cells by blocking the abnormalities.
Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT): This treatment is the combination of a drug that targets cancer cells with a small amount of a radioactive substance. PRRT delivers radiation to the cancer cells.
Medications to control excess hormones: The type of neuroendocrine tumor that releases excessive hormones can be treated with medications. Therefore, the medication aims to control the signs and symptoms of the disease.
Radiation therapy: The treatment of radiation therapy includes the usage of robust energy beams, such as X-rays and protons, to kill tumor cells. If the doctor is not using surgery as a treatment option, radiation therapy can work to treat the NET.