A small butterfly-shaped gland, the thyroid gland throws a huge impact on your overall health by being located at the base of your front neck. First and foremost, the thyroid gland is responsible for the functioning of every organ in our body. In the scenario when the gland does not work properly, it can disconnect the body’s synchronization. Difference between Hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism
By playing a crucial role in the most bodily functions, the thyroid gland monitors metabolism and body temperature too.
Therefore, a disbalance in thyroid functioning could make your metabolism go up or down. A problem in metabolism functioning defines the two conditions hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. There is a difference in both these conditions which we are going to discuss further in this article.
Difference Between Hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism
The thyroid gland is known to be an endocrine organ that secretes thyroxin (T4) and tri-iodothyronine (T3).
Basically, these secretions serve to sustain the metabolic functions of the human body.
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is the condition of the excess of thyroid hormones. This follows an dispatch in the expected actions of the body. Mainly, the condition of hyperthyroidism occurs when someone ingests excessive iodine or thyroxin. The problems a hyperthyroidism patient will face are:
- Loss of weight
- Agitation
- Tremor
- Heat intolerance
- Loss of libido
- Irregular menstrual bleeding
- Psychosis
- Excessive sweating
The Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism Will Include:
- Unintentional weight loss
- Increased appetite
- Nervousness, anxiety, and irritability
- Fine trembling
- Sweating
- Rapid heartbeat (tachycardia)
- Irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia)
- Pounding of your heart (palpitations)
- Changes in menstrual patterns
- Increased sensitivity to heat
- Changes in bowel patterns
- An enlarged thyroid gland (goiter)
- Fatigue, muscle weakness
- Difficulty sleeping
- Skin thinning
- Hair loss
- Nail Deformities
Hyperthyroidism can be treated by diagnosing the causes of the condition. The treatments of Hyperthyroidism includes:
Radioactive iodine: It involves consuming a pill or liquid that meant to get into your bloodstream to counteract the overactive thyroid cells.
Anti-thyroid medicine: This helps your body to suppress the production of thyroid hormones to some extent.
Surgery: Surgery includes removing most of your thyroid gland.
Beta-blockers: This kind of drugs decrease your heart rate and diminish tremors and anxiety.
Hypothyroidism
When your body lacks thyroid hormones, it is known as hypothyroidism. A shortage of these hormones affects the expected actions. Hypothyroidism might happen due to a congenital cause, iatrogenic, or by radiation.
The problems a hypothyroidism patient will face are:
- Dry skin
- Increased sensitivity to cold
- Constipation
- Heavy menstrual bleeds
- Weight gain
- Depression
- Lethargy
The symptoms of Hypothyroidism will include:
- Fatigue
- Puffy face
- Hoarseness
- Muscle weakness
- Elevated blood cholesterol level
- Muscle aches, tenderness, and stiffness
- Pain, stiffness or swelling in your joints
- Thinning hair
- Impaired memory
- Enlarged thyroid gland (goiter)
- Slowed heart rate
- Depression
The condition of hyperthyroidism might be a result of radiation therapy, Autoimmune disease, hyperthyroidism treatments, thyroid surgery, and certain medications.
Treatment for Hypothyroidism
However, hypothyroidism is a lifelong condition, proper medication can reduce the symptoms.
The best treatment for this condition is levothyroxine (Levothroid, Levoxyl). Taking this medication can deliver adequate levels of thyroid hormone to your blood. What happens is that levothyroxine restores your hormones level and thus, let the symptoms of hypothyroidism get disappear.
Hyperthyroidism Versus Hypothyroidism
Till now you might have understood what hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism is. There are many similarities between them. More precisely, you can check below the hypothyroidism vs hyperthyroidism chart to know the difference between both of them.
Difference between hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism
| Hyperthyroidism | Hypothyroidism | |
| About | Also known as overactive thyroid. Occurs when thyroid gland overproduces thyroid hormones, thus accelerating the body’s natural functions. | Also known as underactive thyroid. Occurs when thyroid glance is not secreting enough thyroid hormones, which leads to the slowing-down of the body’s natural functions. |
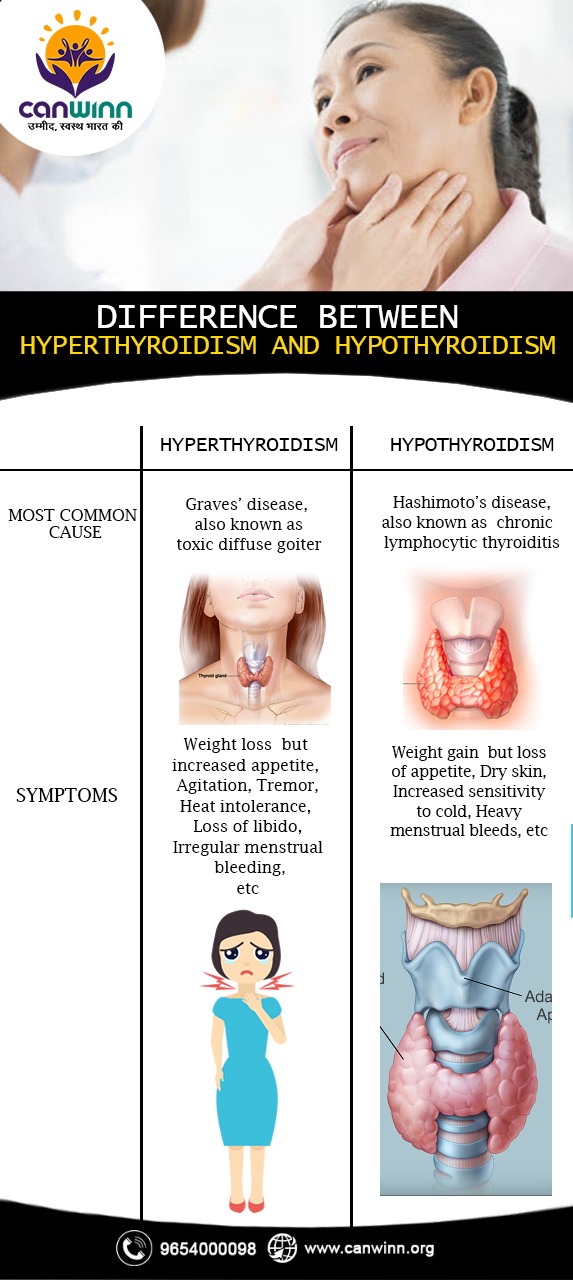
| Most Common Cause | Graves’ disease, also known as toxic diffuse goiter | Hashimoto’s disease, also known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis |
| Other Causes | Thyroiditis, iodine deficiency, medication, thyroid nodules. | Thyroiditis, too much iodine, medication, genetics, hyperthyroidism treatments. |
| Diagnosis | Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) test, thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI) test, thyroid scan, radioactive iodine uptake test. | Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) test, thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI) test, thyroid scan, radioactive iodine uptake test. |
| Treatment | Antithyroid medication (e.g, Methimazole) to slow overactive thyroid and, sometimes, beta blockers (e.g., Propranolol) to alleviate symptoms. | Synthetic thyroid hormone (e.g., Levothyroxine) or carefully monitored iodine supplementation. |
| Occurrence | Less common. Women more likely to suffer due to effects of pregnancy. | More common. Women more likely to suffer due to effects of pregnancy. |
| Appetite | Weight loss but increased appetite | Weight gain but loss of appetite |
| Pulse | Tachycardia | Bradycardia |
| Skin | Warm and moist | Dry and coarse |
| Hair | Fine and soft | Thin and brittle |
| Temperature Intolerance | Heat intolerance | Cold intolerance |
| In Pets | Occurs in about 2% of cats over 10 years of age and in 1-2% of dogs | Can occur, but less common than hyperthyroidism |
| ICD-10 | E05 | E03.9 |
| ICD-9 | 242.90 | 244.9 |
| MedlinePlus | 000356 | 000353 |
| eMedicine | med/1109 | med/1145 |
| DiseasesDB | 6348 | 6558 |
| MeSH | D006980 | D007037 |